Connect with cloudflared
Cloudflare Tunnel is an outbound-only daemon service that can run on nearly any host machine and proxies local traffic once validated from the Cloudflare network. User traffic initiated from the WARP endpoint client onramps to Cloudflare, passes down your Cloudflare Tunnel connections, and terminates automatically in your local network. Traffic reaching your internal applications or services will carry the local source IP address of the host machine running the cloudflared daemon.
To connect your private network:
-
Log in to Zero Trust ↗ and go to Networks > Tunnels.
-
Select Create a tunnel.
-
Choose Cloudflared for the connector type and select Next.
-
Enter a name for your tunnel. We suggest choosing a name that reflects the type of resources you want to connect through this tunnel (for example,
enterprise-VPC-01). -
Select Save tunnel.
-
Next, you will need to install
cloudflaredand run it. To do so, check that the environment under Choose an environment reflects the operating system on your machine, then copy the command in the box below and paste it into a terminal window. Run the command. -
Once the command has finished running, your connector will appear in Zero Trust.
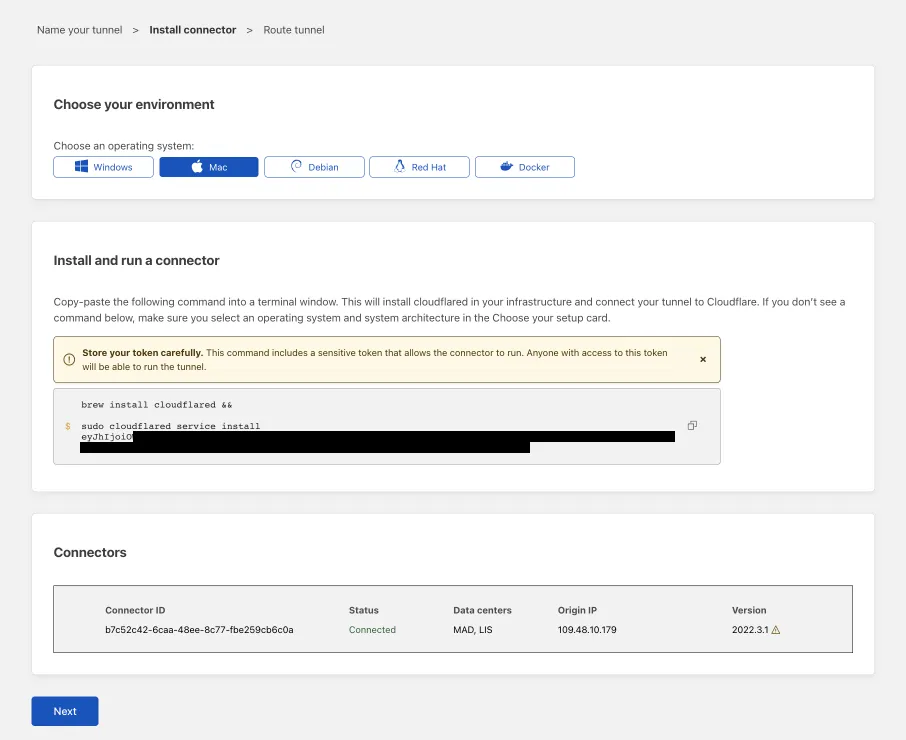
-
Select Next.
-
In the Private Networks tab, enter the CIDR of your private network (for example,
10.0.0.0/8). -
Select Save tunnel.
-
Add the following permission to your
cloudflare_api_token↗:Cloudflare Tunnel Write
-
Create a tunnel using the
cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflare↗ resource.resource "cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared" "example_tunnel" {account_id = var.cloudflare_account_idname = "Example tunnel"config_src = "cloudflare"} -
Route the CIDR of your private network through the tunnel using the
cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared_route↗ resource:resource "cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared_route" "example_tunnel_route" {account_id = var.cloudflare_account_idtunnel_id = cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared.example_tunnel.idnetwork = "10.0.0.0/8"comment = "Example tunnel route"} -
Get the token used to run the tunnel:
data "cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared_token" "tunnel_token" {account_id = var.cloudflare_account_idtunnel_id = cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared.example_tunnel.id}If your host machine is not managed in Terraform or you want to install the tunnel manually, you can output the token value to the CLI.
Example: Output to CLI
- Output the tunnel token to the Terraform state file:
output "tunnel_token" {value = data.cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared_token.tunnel_token.tokensensitive = true}
- Apply the configuration:
Terminal window terraform apply - Read the tunnel token:
Terminal window terraform output -raw tunnel_tokeneyJhIj...
Alternatively, pass
data.cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared_token.tunnel_token.tokendirectly into your host's Terraform configuration or store the token in your secret management tool.Example: Store in HashiCorp Vault
resource "vault_generic_secret" "tunnel_token" {path = "kv/cloudflare/tunnel_token"data_json = jsonencode({"TUNNEL_TOKEN" = data.cloudflare_zero_trust_tunnel_cloudflared_token.tunnel_token.token})} - Output the tunnel token to the Terraform state file:
-
Install
cloudflaredon a host machine in your private network and run the tunnel:-
Download and install ↗
cloudflared. -
Run the following command:
Terminal window sudo cloudflared service install <TUNNEL_TOKEN>
-
Download and install
cloudflared. -
Open Command Prompt as administrator.
-
Run the following command:
cloudflared.exe service install <TUNNEL_TOKEN>
-
Download and install
cloudflared. -
Open a terminal window and run the following command:
Terminal window sudo cloudflared service install <TUNNEL_TOKEN>
-
Open a terminal window.
-
Run the following command:
Terminal window docker run cloudflare/cloudflared:latest tunnel --no-autoupdate run --token <TUNNEL_TOKEN>
-
All internal applications and services in this IP range are now connected to Cloudflare.
- Segregate production and staging traffic among different Cloudflare tunnels.
- Add a
cloudflaredreplica to another host machine for an additional point of availability. - Distribute access to critical services (for example, private DNS, Active Directory, and other critical systems) across different tunnels for blast-radius reduction in the event of a server-side outage.
- Enable notifications in the Cloudflare dashboard to monitor tunnel health.
- Monitor performance metrics to identify potential bottlenecks.
- Update
cloudflaredregularly.
Was this helpful?
- Resources
- API
- New to Cloudflare?
- Products
- Sponsorships
- Open Source
- Support
- Help Center
- System Status
- Compliance
- GDPR
- Company
- cloudflare.com
- Our team
- Careers
- 2025 Cloudflare, Inc.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Report Security Issues
- Trademark